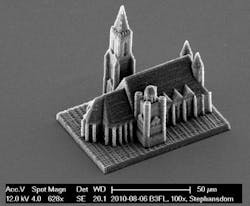
3D printer uses two-photon lithography for nanoprecision
Vienna, Austria--3D objects only microns in size can be fabricated with a 3D printer that relies on two-photon lithography for its precision. The device, created by researchers at the Vienna University of Technology (TU Vienna), benefits from an orders-of-magnitude improvement in speed arising from the researchers' innovations. This opens up completely new areas of application, such as in medicine.
Fast mirrors
The 3D printer uses a liquid resin that is hardened by a focused laser beam guided through the resin by scanning mirrors. The result is a hardened line of solid polymer a few hundred nanometers wide. “Until now, this technique used to be quite slow,” says Jürgen Stampfl from the Institute of Materials Science and Technology at TU Vienna. “The printing speed used to be measured in millimeters per second; our device can do five meters in one second.”
Several new ideas were combined to achieve the higher speed. “It was crucial to improve the steering mechanism of the mirrors,” says Jan Torgersen, also of TU Vienna. The mirrors are continuously in motion during the printing process; the acceleration and deceleration-periods have to be tuned very precisely to achieve high-resolution results at a record-breaking speed.
Chemistry plays an important role too. “The resin contains molecules which are activated by the laser light. They induce a chain reaction in other components of the resin, so-called monomers, and turn them into a solid,” says Torgersen. These initiator molecules are only activated if they absorb two photons at once, which only happens in the very center of the beam where the intensity is highest. In contrast to conventional 3D-printing techniques, solid material can be created anywhere within the liquid resin rather than on top of the previously created layer only. Therefore, the working surface does not have to be specially prepared before the next layer can be produced, which saves a lot of time. A team of chemists led by Robert Liska at TU Vienna developed the suitable ingredients for this special resin.
TU Vienna scientists are now developing biocompatible resins for medical applications that can be used to create scaffolds to which living cells can attach themselves, enabling systematic creation of biological tissues.

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.