Management and Optimization of Ultrafast Broadband Pulses from Your Laser
Virtually every application of visible and near-IR lasers inevitably utilizes one or more glass lenses as well as other transmissive optics. But with femtosecond lasers, the dispersion caused by these transmissive elements broadens (stretch) the pulse width and distorts the temporal shape of the pulses. However, most applications of femtosecond pulses require to minimize or precisely offset this pulse broadening in order to deliver the shortest possible pulse width in the experiment. This comprehensive whitepaper explains how to rigorously calculate dispersion effects and presents strategies to minimize the real pulse width.
In a high performance ultrafast laser, the pulse width is very close to “transform limited” where it is defined by the time-bandwidth relationship. Pulse broadening occurs in downstream optics because of dispersion where the interaction between the light and the transmission medium (glass, CaF2, or air) is wavelength dependent. Specifically, the group velocity of light in any medium except vacuum depends on the wavelength. (This manifests as a wavelength dependence for the effective refractive index of that medium.) Femtosecond pulse can have a bandwidth > 100 nanometers, with the longer wavelength components of the pulse traveling through the optic(s) more rapidly than the shorter wavelength components. This effect is quantified by the Group Velocity Dispersion (GVD) and higher order dispersion terms, and the affected pulses are said to be “chirped”.
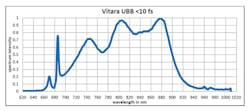
Typical spectral amplitude of pulse from Vitara UBB (Transform-limited pulse duration = 7 fs)
In this whitepaper, we show how and why GVD becomes an ever larger problem as applications move to shorter pulse widths. We show which materials cause least GVD. We describe how to calculate the various (e.g., second order, third order) contributions to GVD. We also discuss the importance of using a well-designed pre-compensation scheme where the pulses are pre-stretched with negative chirp to carefully offset the positive chirp of the downstream components.
Example of broadening of a 7 fs Pulse through Different Materials