OPTICAL TWEEZERS: Imaging lets optical tweezers ‘feel the force’
A low-cost, imaging-based force-feedback device has been created that allows users to perceive real Brownian motion and viscosity when using optical tweezers; in effect, the user can “feel the force” exerted as objects are manipulated by a trapped bead.1 The device is the result of a collaborative effort by researchers from the Université Pierre et Marie Curie (Paris, France), CEA Laboratoire Interfaces Sensorielles (Fontenay-aux-Roses, France), the University of Glasgow (Glasgow, Scotland), and the University of Bristol (Bristol, England).
Optical tweezers are in widespread use for the micromanipulation of objects in cell biology, nanotechnology, and microengineering applications. Unfortunately, use of a mouse or standard joystick does not let the operator know what force is being exerted, and more-sophisticated force-feedback methods such as haptic guidance—using an artificial force field—are in their infancy. Recognizing that optical tweezers can also be used for force measurements, the research team seized on the opportunity to use the actual forces acting on a bead (measuring the magnitudes of the forces by analyzing images from a high-speed video camera), and coupled those force measurements to a low-cost commercial haptic interface—the Falcon by Novint (Albuquerque, NM).
Imaging plus force measurement
By placing the camera in the back-reflected optical path behind an optical-trap steering mirror, a camera sensor or quadrant photodiode is used to track the displacement of the trapped object from the center of the trap. The trapping force is directly proportional to this displacement, so it is multiplied by the trap’s stiffness to calculate the force. These values are then fed back as a force on the operator’s hand by motorized axes in the haptic interface. The handle of the haptic device is even ball-shaped, giving the operator the illusion of touching the microsphere that is being trapped.
In the experimental setup, trapping is performed by an 830 nm, 1.3 W Ti:sapphire laser coupled by a micrometer-driven mirror that allows positioning of the trap within the field of view. An inverted microscope focuses the beam and images particle motion. Two CMOS-sensor-based cameras are used in the setup: the first is in its typical location just after the objective lens, unaffected by beam-steering optics and providing a wide field of view; the second camera is in the back-reflected optical path and images trapped objects as previously described. The object in the trap fits into a 50 × 50-pixel region on the camera (corresponding to about 7 µm) and can be tracked on-the-fly at a rate of 1 kHz, which is fast enough to feel smooth. The picoNewton-size forces are then scaled by a factor of 1012 for the Novint Falcon interface, which exerts a maximum force of 9 N on the user’s hand. Currently, the interface is limited to two-dimensional particle motion.
Feeling the force
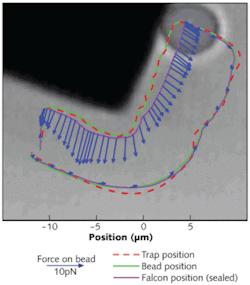
The interface was tested subjectively by having an operator experience the force of the optical trap on 5-µm-diameter beads using the haptic-device handle as the beads interacted with some silicon cubes 100 µm in size (see figure). The researchers said that the system allowed the user to feel the reaction force when the bead was in contact with the cube, and to feel its viscous drag as it was moved through the suspension solution.
“The way things scale between your hands and the microscope slide is strange–distance shrinks by a factor of about 1000, but force is 1012 times smaller. That means it’s very easy for the system to become unstable, so we had to optimize the system to run as fast as possible to keep it stable,” said Richard Bowman, a Ph.D. student at the University of Glasgow. “In the future, we’d like to replace the mirror with a spatial light modulator to add the third dimension and allow multiple traps, though that makes the force measurement harder as we won’t have the ‘de-scanned’ camera where the trap position is always at the center of the image.”
REFERENCE
- C. Pacoret et al., Optics Express 17(12) p. 10259 (June 8, 2009).

Gail Overton | Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.