Fermionic-noise images show 'spooky action at a distance'
Colorado researchers who reported the first observation of a fermionic condensate a little over a year ago have most recently used it to image quantum entanglement—or what Einstein referred to as “spooky action at a distance”—between pairs of laser-cooled potassium atoms. Fermionic condensates are also expected to provide clues for understanding the yet to be explained phenomena of high-temperature superconductivity, as well as the yet-to-be-achieved phenomena of room-temperature superconductivity. The technique used in the most recently reported experiments, based on measuring atom shot noise in a fermionic condensate, may ultimately provide a methodology for actually testing many of the ideas behind quantum physics.
Fermions (elementary particles with half-integer spin that form electrons, protons, and neutrons) can condense into fermionic condensates and behave according to Fermi-Dirac statistics, just as bosons (elementary particles with integer spin that form photons) can condense into Bose-Einstein condensates and behave according to Bose-Einstein statistics. Both of these quantum-mechanical statistical expressions are closely related to the classical Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas. Unlike bosons, however, which can densely populate a single quantum state, fermions are regulated by the Pauli exclusion principle, which explains the discrete nature of atomic electron shells, but also prevents identical fermions from simultaneously occupying the same quantum state.
So while one might expect laser-cooled bosons to condense into a superfluidic Bose-Einstein condensate, the condensation of highly individualistic fermions into a superfluidic fermionic condensate is actually counterintuitive. Nevertheless, early last year a joint research team headed by Deborah Jin at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), JILA, and the University of Colorado at Boulder (all of Boulder, CO), used a magnetic field near a Feshbach resonance (where a molecular state has the same energy as colliding atoms) to induce laser-cooled fermions (potassium atoms) to pair up in a manner similar to the way in which electrons form the “Cooper pairs” that enable superconductivity in metals and alloys.1
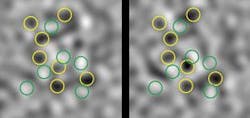
In the current work, Jin’s team has used a similar method to image noise distributions in entangled potassium atom pairs (see figure).2 The atoms were trapped in two groups, one group in the ground energy state of potassium and the other in the next highest energy state. Sweeping a Feshbach resonance magnetic field across the trapped mixture of the two groups caused atoms at different energy levels to pair up in weakly bound molecules. Subsequently increasing the magnetic field led the molecules to dissociate but not before creating quantum entanglements between atom pairs.
Long-range effects
Time-of-flight (TOF) absorption images of the noise distribution in the atom groups were taken by illuminating the atoms with a laser beam and recording shadow images of the scattered light on a CCD camera. Overlapping atom-pair correlations were observed by successive laser illuminations, each tuned to one of the two group energy levels. Displaced atom-pair correlations were also observed by using a radio-wave pulse to split the two groups into pairs of entangled atoms flying apart with equal momentum but in opposite directions. In both overlapping and displaced cases, noise distributions from the two energy-level groups yielded similar patterns, even when (in the second case) the groups were separated by as much as 350 µm. The results appear to offer significant potential for studying a variety of quantum and multiparticle phenomena, including Cooper pairs in an atomic Fermi gas, antiferromagnetic phases, and spin waves in optical lattices. “There are a number of interesting quantum states that are not obviously seen if you just take a picture,” Jin said. “A Fermi condensate, for example, would not show up in an ordinary image. However, correlations between atoms should actually show up in the noise in these images.”
REFERENCES
1. C. A. Regal et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 040403 (Jan. 30, 2004).
2. M. Greiner et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 110401 (March 25, 2005).
About the Author
Hassaun A. Jones-Bey
Senior Editor and Freelance Writer
Hassaun A. Jones-Bey was a senior editor and then freelance writer for Laser Focus World.