Laser levitation and an optical trap enables nuclear recoil spectroscopy
Recognizing the difficulty in measuring smaller nuclear particles using traditional alpha and gamma spectroscopy, scintillation counting, and cloud-chamber detection, researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL; Los Alamos, NM) have developed an alternative measurement method using laser levitation of nuclear particles in an optical trap. Small particle analysis can identify the nuclear isotopes within a sample, which is critical to environmental monitoring and in nuclear forensics of manufacturing facilities.
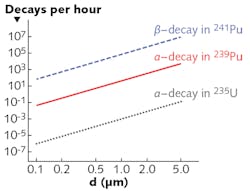
The LANL method determines the isotopic ratios and type of nuclear material by measuring the magnitude and frequency of the recoil (and associated kinetic energy) of a small optically trapped particle as its nuclear material decays. In the decay process for a plutonium oxide (238PuO2) particle (d = 10 nm to 10 µm), for example, a solid particle of diameter d containing nuclear material will decay and emit a daughter atom and radiation that is carried by gamma (γ) photons or by alpha (α) and beta (β) particles. If placed in an optical trap consisting of a 638 nm, 100 mW laser focused to a waist of a few microns, the recoil displacement is measured by position-sensitive photodiodes in real time. The measured displacements can then be used to calculate the kinetic energy of the emitted particles, which is characteristic of the radioactive isotope contained in the trapped sample. Essentially, this unique decay energy can determine the composition of starting nuclear material in the particle. Reference: A. Malyzhenkov et al., Phys. Rev. A, 98, 052103 (2018).
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.